Sci-fi smart bandage promotes healing
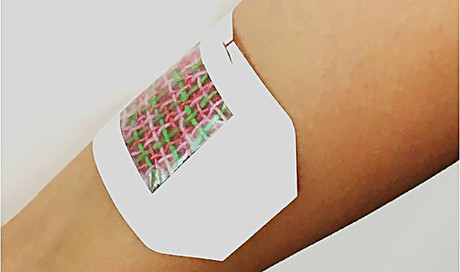
A smart bandage with electrically conductive fibres could eventually heal chronic wounds or battlefield injuries.
The bandage, designed by researchers at University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Harvard Medical School and MIT, consists of electrically conductive fibres coated in a gel that can be individually loaded with infection-fighting antibiotics, tissue-regenerating growth factors, painkillers or other medications.
A microcontroller no larger than a postage stamp, which could be triggered by a smartphone or other wireless device, sends small amounts of voltage through a chosen fibre. That voltage heats the fibre and its hydrogel, releasing whatever cargo it contains.
A single bandage could accommodate multiple medications tailored to a specific type of wound, the researchers said, while offering the ability to precisely control the dose and delivery schedule of those medications. That combination of customisation and control could substantially improve or accelerate the healing process, said Ali Tamayol, assistant professor of Mechanical and Materials Engineering at Nebraska.
“This is the first bandage that is capable of dose-dependent drug release,” Tamayol said. “You can release multiple drugs with different release profiles. That’s a big advantage in comparison with other systems. What we did here was come up with a strategy for building a bandage from the bottom up.
“This is a platform that can be applied to many different areas of biomedical engineering and medicine.”
The team envisions its smart bandage being used initially to treat chronic skin wounds that stem from diabetes. Those wounded in combat might also benefit from the bandage’s versatility and customisability, Tamayol said, whether to stimulate faster healing of bullet and shrapnel wounds or prevent the onset of infection in remote environments.
“Soldiers on the battlefield may be suffering from a number of different injuries or infections,” he said. “They might be dealing with a number of different pathogens. Imagine that you have a variable patch that has antidotes or drugs targeted toward specific hazards in the environment.”
Though the researchers have patented their design, it will need to undergo further testing before going to market.
In the meantime, the researchers are also working to incorporate thread-based sensors that can measure glucose, pH and other health-related indicators of skin tissue. Integrating that capability would allow the team to create a bandage that could autonomously deliver proper treatments.
The authors detailed their design and findings in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
$1bn vaccine and antivenom manufacturing facility opens
A $1 billion cell-based influenza vaccine and antivenom manufacturing facility has opened in...
National concussion clinical guidelines now available
The first Australia- and New Zealand-specific guidelines for all forms of concussion — from...
Doctors criticise "risky prescribing agenda"
The AMA and RACGP have expressed disappointment in the Pharmacy Board of Australia's...

![[New Zealand] Transform from Security Awareness to a Security Culture: A Vital Shift for SMB Healthcare — Webinar](https://d1v1e13ebw3o15.cloudfront.net/data/89856/wfmedia_thumb/..jpg)
![[Australia] Transform from Security Awareness to a Security Culture: A Vital Shift for SMB Healthcare — Webinar](https://d1v1e13ebw3o15.cloudfront.net/data/89855/wfmedia_thumb/..jpg)




