Who am I? Do I have concussion?
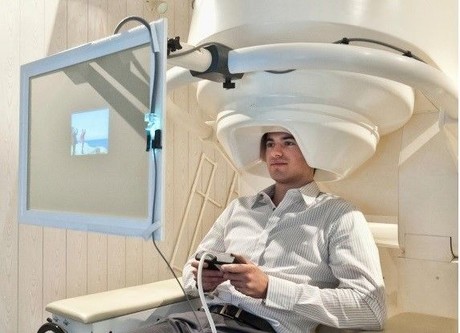
High-resolution brain scans analysed by machine learning algorithms could determine whether a patient has a concussion, according to a new study published in PLOS Computational Biology.
Currently, doctors diagnose concussions according to patient-reported symptoms, which can be challenging and inefficient. Previous studies have used high-resolution imaging to show that concussions cause changes in communication between different brain areas. However, these studies have typically only looked at average changes across groups of patients.
Vasily Vakorin, now of Simon Fraser University, British Columbia, and colleagues (from the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto and Defense Research and Development Canada) investigated whether high-resolution imaging could be combined with machine learning algorithms to detect concussions in the brains of individual patients.
The researchers scanned the brains of men with and without concussion using magnetoencephalography (MEG), which records brain activity at fast time scales. MEG imaging showed that patients with concussions had distinctive changes in communication among areas of their brains.
Then, by employing machine learning algorithms, the scientists were able to use individual brain scans to work backwards and then predict whether a given patient had a concussion or not. They were able to detect concussions with 88% accuracy. This approach also accurately predicted the severity of symptoms reported by individual patients.
“Changes in communication between brain areas, as detected by magnetoencephalography, allowed us to detect concussion from individual scans, in situations wherein typical clinical imaging tools such as MRI or CT fail,” study coauthor Sam Doesburg said.
Future research could refine understanding of the specific neural changes associated with concussions in order to improve detection, inform treatment and monitor recovery.
Non-invasive 'virtual' biopsy for skin cancer diagnosis
Researchers have developed a new imaging method that allows clinicians to analyse the skin...
UTI vaccines could prevent infection for nine years
MV140 is a new vaccine for recurrent UTIs and is administered with two sprays of a...
What's the key to retaining rural GPs?
Understanding doctors' decisions to stay or leave, once recruited, could provide insights on...










